| python paramiko exec | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › exec 用法 › python paramiko exec |
python paramiko exec
|
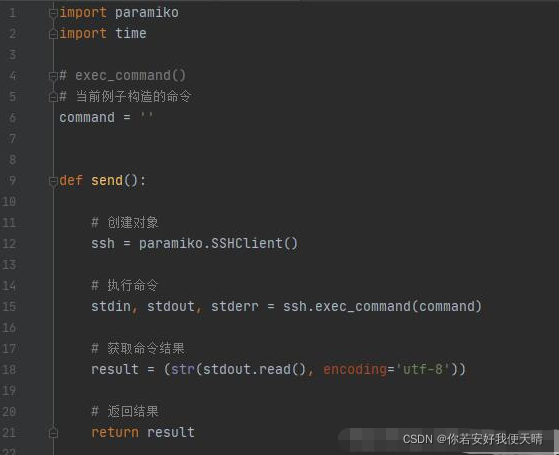
paramiko模块exec_command()函数是将服务器执行完的结果一次性返回给你; invoke_shell()函数类似shell终端,可以将执行结果分批次返回,看到任务的执行情况,不会因为执行一个很长的脚本而不知道是否执行成功 exec_command():
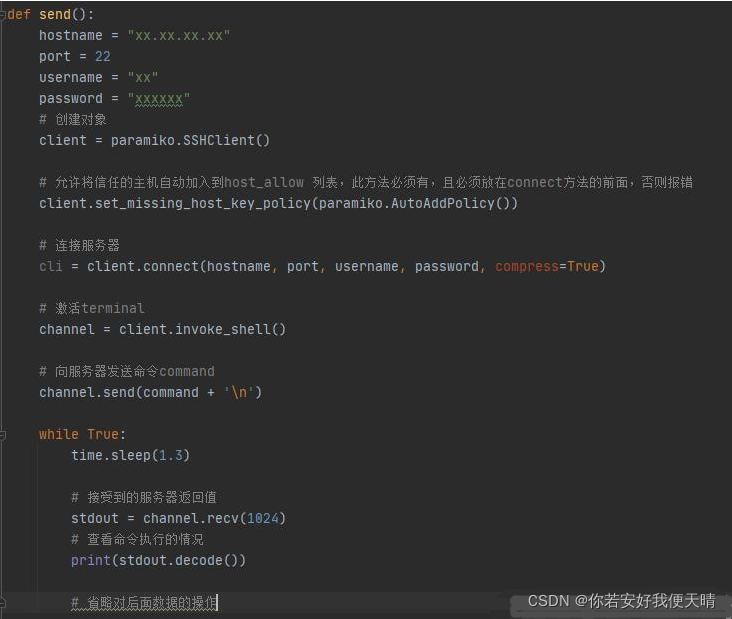
invoke_shell()
参考:第二篇:ssh.invoke_shell() 切换root出现的新问题 - FelixApff - 博客园 SSHClient类打包了.Transport,.Channel,.SFTPClient来满足多方面的认证和传输的要求,下面来看看部分用法。 一、类实例化 ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()实例化一个SSHClient类的对象。 实例化的时候做了些什么呢?查看一下paramiko版本2.8.1中的源码: def __init__(self): """ Create a new SSHClient. """ self._system_host_keys = HostKeys() self._host_keys = HostKeys() self._host_keys_filename = None self._log_channel = None self._policy = RejectPolicy() self._transport = None self._agent = None可以看到构造函数中,对新对象的部分属性进行了初始化,如主机公钥、日志、拒绝策略、传输方式和代理这些。 其中关于公钥,根据在RFC4251中的定义: Each server host SHOULD have a host key. Hosts MAY have multiple host keys using multiple different algorithms. Multiple hosts MAY share the same host key. If a host has keys at all, it MUST have at least one key that uses each REQUIRED public key algorithm (DSS [FIPS-186-2]). The server host key is used during key exchange to verify that the client is really talking to the correct server. For this to be possible, the client must have a priori knowledge of the server's public host key.每个服务器都有公钥,在编写链接功能时,在和服务器建立链接之前,要进行准备公钥的操作。 二、自动添加公钥的方法 当链接新的服务器时,我们不一定会准备好了公钥。这时如何处理: ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy()这个函数可以用来处理针对未知主机时,使用什么样的策略。阅读源码中的注释: * A **policy** is a "policy class" (or instance thereof), namely some subclass of `.MissingHostKeyPolicy` such as `.RejectPolicy` (the default), `.AutoAddPolicy`, `.WarningPolicy`, or a user-created subclass.可以看出如果不设定的话,默认是拒绝建立链接的。所以我们可以加入以下语句: ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())这条语句就是当链接到一个未知的主机时设置策略为,自动添加公钥策略。 如果不添加这条语句,则需要注意:链接新的服务器由于没有添加公钥,会产生报错。 三、建立链接 进行建立链接的操作: ssh_client.connect(hostname=server_ip, port=server_port, username=server_username,password=server_password)通过用户名和密码的方式登录主机,这种方法比较常用。不过用秘钥登录,则更方便和安全。 paramiko是怎样建立链接的呢?如下: for af, addr in to_try: try: sock = socket.socket(af, socket.SOCK_STREAM) if timeout is not None: try: sock.settimeout(timeout) except: pass retry_on_signal(lambda: sock.connect(addr)) # Break out of the loop on success break except socket.error as e: # Raise anything that isn't a straight up connection error # (such as a resolution error) if e.errno not in (ECONNREFUSED, EHOSTUNREACH): raise # Capture anything else so we know how the run looks once # iteration is complete. Retain info about which attempt # this was. errors[addr] = eparamiko通过socket库,将重复尝试对主机进行建立链接的操作。 根据retry_on_signal()函数的源码: def retry_on_signal(function): """Retries function until it doesn't raise an EINTR error""" while True: try: return function() except EnvironmentError as e: if e.errno != errno.EINTR: raise当出现除了系统中断以外的异常时,会让程序停止尝试。 四、执行命令 可以选择.exec_command或者.invoke_shell函数执行命令。 def resource_query_get(connection, query_command, pty_status=False): standard_in, standard_out, standard_err = connection.exec_command(query_command, get_pty=pty_status) return standard_out可以将需要执行的多条命令,作为一个数组循环调用函数,以自动完成预定的任务。 另外,需要注意如sar,top等非即时返回结果的命令,需要加上pty_status=True的参数。pty_status为True时,程序向服务器请求了一个伪终端。例如下面这种情况: server_pty_command_list = ["sar -u 2 5 | sed -n '9p' | awk '{print $3}'"] for query_command in server_pty_command_list: record_file(resource_query_get(connection, query_command, True))我们需要取回CPU使用率的5秒内的平均取样,这条命令需要等待5秒后才会有结果,如果没有把pty_status设置为Ture,就无法取回值。 看下关于pty_status的注释: Request a pseudo-terminal from the server. This is usually used right after creating a client channel, to ask the server to provide some basic terminal semantics for a shell invoked with `invoke_shell`. It isn't necessary (or desirable) to call this method if you're going to execute a single command with `exec_command`.设计者建议也可以使用invoke_shell函数来完成具有交互需求的功能。所以可以根据实际需要来选择用法,需要即时执行命令返回结果的建议使用exec_command,更复杂的交互需求则建议使用invoke_shell函数完成。 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66158540/article/details/123261304 |
【本文地址】